Is X-raying children’s teeth dangerous?
Dear parents, we are often asked whether an X-ray examination is necessary to diagnose cavities between the teeth. Behind this question is the concern many parents have about X-ray radiation and its possible effects on their child. Our goal is to provide you with information that will help you make an informed decision if your child needs to have a dental X-ray taken.

Interview with Dr. Silvia Meidner
I am a pediatric dentist with passion and have been working at the children’s dental practice Lachzahn in Munich-Trudering since 2012. As both a mother and a dentist, it is very important to me to educate parents about the importance of their children’s dental health and to build a strong foundation for close cooperation.
Is X-raying really necessary at the children’s dentist?
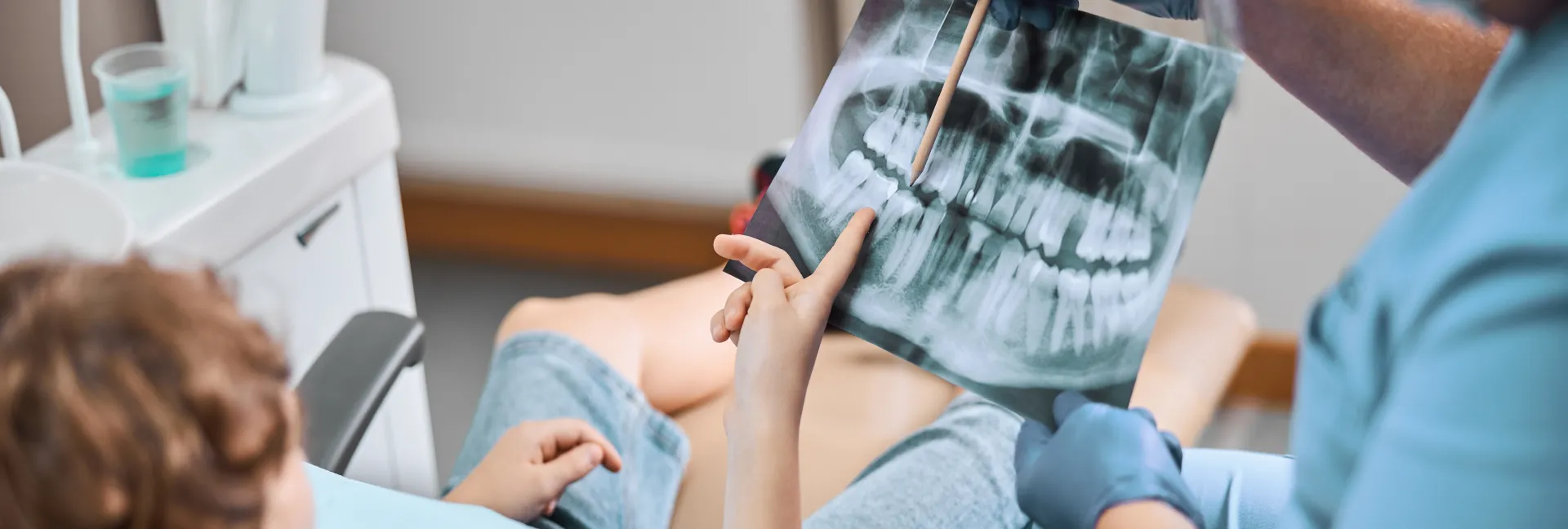
First of all, you should know that, as pediatric dentists, we carefully assess whether an X-ray is necessary for your child or not. In certain cases, an X-ray of the children’s teeth is needed to make more precise statements and to ensure an accurate diagnosis. But here’s the good news: in modern pediatric dental practices, X-rays are no longer taken using analog techniques, but digitally and intraorally. This has the great advantage that the radiation dose is reduced by an average of 90% compared to traditional analog X-rays.
Dental X-rays in Children – PRO
Early Diagnosis
In certain cases, X-rays of children’s teeth allow cavities, misaligned teeth, or developmental disorders to be diagnosed and treated much earlier, before bigger problems arise.
More Accurate Diagnosis
With the help of X-ray images, the pediatric dentist obtains a detailed view of the teeth and jawbone. This allows a better understanding of the exact position of the teeth and the structure of the jaw, leading to a more precise diagnosis.
Monitoring Function
X-rays can also be used to document the growth and development of the teeth and jaw over time, helping to track the success of treatment more effectively.
Dental X-rays in Children – CONTRA
Radiation Exposure
X-rays expose children to a low dose of radiation, which can pose a potential risk if repeated over time. Therefore, the number of X-rays should still be limited to what is strictly necessary.
Radiation Exposure
X-rays can incur additional costs, which may not be covered by all insurance plans. Parents should be informed about the financial implications before agreeing to have X-rays taken.
Is the Radiation Dose from Dental X-rays High?
The radiation dose from digital X-rays is very low. A single dental X-ray corresponds to only 0.6 µSv! To put this into perspective, let’s first consider the radiation we are exposed to daily. No matter where we are, we are constantly exposed to natural sources of radiation.
The best-known source is cosmic radiation. It comes from outer space, for example from the sun or the Milky Way, and reaches the Earth. Its intensity depends on altitude, because the protective layer of air around the Earth is thinner at higher elevations. Traveling by airplane or climbing a mountain increases radiation exposure. Pilots and flight attendants are among the occupational groups with the highest radiation exposure.
On average, cosmic radiation at ground level results in an effective dose of about 300 µSv per year. Inside an airplane at 10 to 12 kilometers altitude, a typical dose rate is 5 µSv per hour. On a flight from Frankfurt to Tokyo, this corresponds to a radiation exposure of roughly 60 µSv.
Less well known is terrestrial radiation. It originates from natural radionuclides formed before the solar system and still present due to their long half-life. The most well-known radionuclide is radon, a radioactive noble gas found in small concentrations almost everywhere. Radon is produced from the decay of uranium. On average, natural radiation sources give humans an effective dose of about 2.4 mSv per year worldwide, about half of which comes from radon.
Gänzlich unbekannt ist, dass auch das Rauchen von Tabak Strahlung, genauer gesagt α-Strahlung, verursacht. Das Rauchen von täglich 20 Zigaretten führt zu einer jährlichen Strahlenbelastung von 290 µSv.
Anhand dieser Daten kann man erkennen, dass eine zahnärztliche Röntgenaufnahme selbstverständlich eine Strahlenbelastung verursacht. Aber mit einer Strahlung von von 0,6 µSv im Vergleich mit den o. g. Strahlungen aber eine sehr geringe Dosis darstellt.
1 Sv [Sievert] ist dabei die Einheit der sog. „Äquivalentdosis“ und entspricht einer Energieabsorption von 1 Joule/kg. Die Äquivalentdosis gibt die Teilkörperdosis an und berücksichtigt die unterschiedliche biologische Wirksamkeit verschiedener Strahlenarten.

Is X-raying dangerous? – My Conclusion
It should not be forgotten that any radiation can have unpredictable effects on body cells. Therefore, the pros and cons of X-rays should always be carefully weighed.
However, when you consider that a single dental X-ray produces the same amount of radiation as a six-hour stay in Germany or an eight-minute flight, it becomes clear that dental X-rays are not really dangerous. In many cases, they even contribute to the long-term dental health of your child.